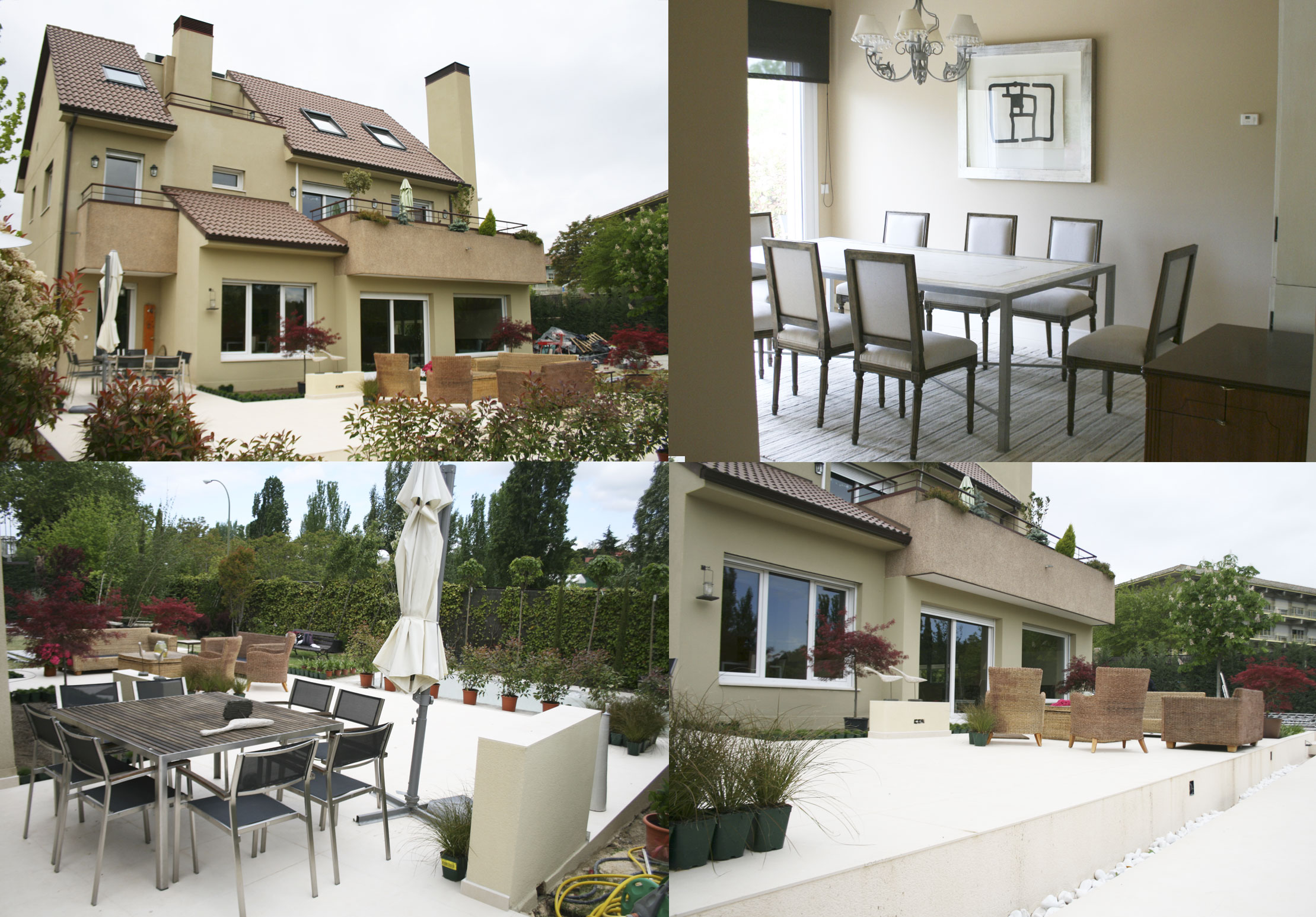
Aging in place modifications symbolize critical changes made to residential environments to assist older adults keep independence, safety, and luxury within their own houses as they age. These adaptations not solely improve day-to-day living but additionally reply proactively to mobility challenges, sensory impairments, and continual well being situations that usually emerge with growing older. Implementing thoughtful modifications reduces fall risks, will increase property accessibility, and minimizes the need for costly institutional care. When guided by established building codes and universal design rules, these upgrades enhance long-term property worth and bolster the homeowner's quality of life profoundly.
Understanding the Core Principles of Aging in Place Modifications
Before choosing specific modifications, comprehending the foundational targets and design philosophies of aging in place strategies is crucial. These ideas dictate how areas adapt to evolving physical and cognitive wants while maximizing comfort and autonomy.
The Concept of Universal Design and Its Relevance
Universal design refers to creating environments usable by all people with out the necessity for adaptation or specialised design. Unlike accessible design, which targets incapacity accommodations instantly, universal design fosters inclusivity for a variety of skills, making it a cornerstone of aging in place. Practical examples embrace zero-step entries, lever handles, and Reforma Residencial ample clearance widths that accommodate walkers or wheelchairs. Employing universal design will increase market appeal and future-proofs properties by permitting aging occupants and diverse visitors to navigate areas safely and easily.
Safety-Focused Modifications: Addressing Fall Prevention and Emergency Accessibility
Falls are a leading explanation for injury amongst older adults, making security options paramount. Non-slip flooring materials, properly positioned seize bars, and enough lighting cut back hazards dramatically. These changes solve pain points related to restricted mobility and sensory decline. Additionally, emergency access concerns, similar to wider doorways and entry ramps, be certain that first responders can help promptly throughout crises. Compliance with pointers like the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and native building codes ensures modifications meet minimum security thresholds.

Enhancing Comfort Through Ergonomic and Sensory Adaptations
Ergonomic variations cater to diminished energy and adaptability, similar to adjustable countertops or seating with acceptable height and help. Sensory solutions handle imaginative and prescient and listening to impairments, incorporating features like contrasting shade schemes, tactile indicators, and amplified doorbells or alarms. These design choices mitigate frustration, improve usability, and considerably enhance emotional well-being by promoting a sense of normalcy and management within the residence.
Critical Areas for Aging in Place Modifications and Their Specialized Solutions
For an aging-friendly residence, focused adaptations in particular areas resolve the most common mobility and safety challenges skilled by older adults. Each house warrants distinct consideration and customised modifications for max impact.
Entryways and Exits—Facilitating Barrier-Free Access
The major challenge at entrances and exits is overcoming step heights, slender doorways, and uneven surfaces, which pose tripping hazards and restrict wheelchair entry. Solutions corresponding to zero-threshold doorways, stable ramps constructed with slip-resistant materials, and automatic door Reforma Residencial openers guarantee easy, independent ingress and egress. Enhancing lighting and including handrails improve security throughout evening or low-vision conditions. These modifications alleviate anxiousness about leaving or returning residence, encouraging social engagement and independence.
Bathroom Modifications—Prioritizing Hygiene and Stability
Bathrooms frequently current the best risk of falls as a outcome of moist surfaces and limited support structures. Installing walk-in showers with grab bars, built-in seating, and anti-scald valves addresses stability and temperature management issues. Elevated or comfort-height bogs and sink cabinetry with knee clearance assist customers with mobility aids. These nuanced adjustments empower older adults to maintain personal hygiene with dignity whereas significantly lowering caregiver help dependence and emergency healthcare costs.
Kitchen Adaptations—Sustaining Nutrition and Independence
The kitchen combines multifaceted challenges: reaching high cupboards, maneuvering inside tight spaces, and safely operating home equipment. Aging in place modifications embody lowered countertops and sinks, pull-out cabinets, and lever faucets to facilitate ease of use. Appliances equipped with easy interfaces, automatic shut-off features, and clear shows fight cognitive and sensory limitations, reducing accident risks. Well-planned kitchens encourage ongoing capability to organize meals independently, which is crucial to well being and psychological well-being.
Living Spaces and Bedrooms—Ensuring Accessibility and Comfort
Open ground plans that allow walker or wheelchair mobility, along with strategic furniture placement, assist create clear circulation paths. Adjustable beds, easily reachable electrical shops with rocker switches, and sensible house integrations like voice-activated lighting amplify ease of daily living. Including multiple seating choices and ambient lighting supports sensory needs and offers rest opportunities, promoting restful sleep and general life satisfaction.
Materials, Technologies, and Equipment That Elevate Aging in Place
Material choices and fashionable technology investments play integral roles in making properties safer, extra convenient, and adaptable to altering talents.
Durable, Non-Slip Surfaces and Maintenance Considerations
Selecting flooring and wall materials that resist slips, stains, and wear optimizes safety and longevity. Textured vinyl, rubber flooring, and handled hardwood optimize traction underfoot. Choosing finishes which might be simple to clean reduces the bodily effort required for maintenance, a big quality-of-life enhancer for aging residents and their caregivers.
Assistive Devices and Smart Home Technologies
Incorporating home automation systems corresponding to voice-controlled lighting, thermostat changes, and door locks reduces bodily pressure and accommodates cognitive challenges. Sensors that monitor movement and detect falls can alert relations or emergency providers instantly. Assistive units like stairlifts, ceiling lifts, and adjustable shelving additional customize a home to individual mobility necessities, https%3a%2f%evolv.e.l.U.pc@haedongacademy.org directly addressing accessibility pain factors and enhancing safety.
Lighting and Acoustic Solutions Tailored for Aging Sensory Needs
Adjustable lighting with options for brightness and shade temperature mimics natural daylight, reducing eye pressure and enhancing mood. Task lighting in kitchens and reading areas helps precision actions, while strategically positioned nightlights stop nighttime disorientation. Acoustic modifications such as sound-absorbing materials and amplified alert systems compensate for declining listening to talents, ensuring communication and security stay unhampered.
Regulatory Compliance and Professional Assessment for Aging in Place
While many modifications goal for person comfort, all should adjust to relevant safety and construction codes to guard householders and uphold resale value.
Understanding Relevant Building Codes and Accessibility Standards
Standards just like the International Building Code (IBC), Fair Housing Act (FHA) guidelines, and ADA specs present baseline necessities for dimensions, clearances, and structural integrity. Aligning modifications with these laws not solely ensures legality but additionally ensures that properties accommodate numerous disabilities and stop future costly remodeling efforts. For instance, minimal doorway widths of 32 inches and accessible toilet configurations are sometimes mandated or really helpful.
The Role of Professional Assessments and Personalized Planning
Engaging licensed aging-in-place specialists (CAPS), occupational therapists, or architects ensures that variations reflect the occupant’s unique useful capabilities and future needs. Comprehensive evaluations identify unseen hazards and tailor solutions that maximize usability and cost-effectiveness. This skilled steerage reduces trial-and-error approaches and supplies holistic, integrated design methods that optimize the house's long-term suitability.
Financial Impact: Cost, Value, and Long-Term Savings of Aging in Place Modifications
The financial issues surrounding aging in place include upfront costs, elevated property worth, and healthcare expense mitigation.
Budgeting for Modifications: Balancing Immediate Investment and Benefits
The value of getting older in place modifications varies widely depending on the complexity and scale of adjustments. Simple upgrades like grab bars and lever handles are comparatively cheap, while major renovations corresponding to stairlifts, bathroom transforming, or home automation require substantial outlays. However, reformas Pequenas early funding in well-planned modifications can stop emergency bills associated to falls, hospitalizations, or untimely assisted living placement, delivering measurable long-term financial savings and stability.
Enhancing Property Marketability and Resale Value
Homes thoughtfully tailored for aging in place attract a broader purchaser base, together with multigenerational families and people with disabilities. Features corresponding to barrier-free entries and accessible loos increase a property’s competitive edge in the market, probably commanding the next worth point. Additionally, documented compliance with accessibility requirements adds transparency and assurance for potential patrons, defending the seller’s interests.
Reducing Healthcare and Caregiver Costs Through Home Modifications
Aging in place diversifications significantly scale back fall incidents, hospital readmissions, and dependence on skilled caregivers. Scientific research verify that well-modified environments immediately correlate with improved physical well being outcomes and psychological well-being. This interprets into fewer emergency visits, delayed or prevented nursing house admissions, and decreased caregiver burnout, benefiting households financially and emotionally.
Final Considerations and Actionable Steps for Successful Aging in Place Adaptations
Implementing growing older in place modifications is a multi-faceted course of that integrates security, comfort, regulatory adherence, and monetary planning to sustain unbiased residing successfully.

Key Takeaways for Homeowners and Professionals
Comprehensive aging in place modifications begin with common design rules prioritizing security and accessibility across all essential residence areas. Critical zones corresponding to entryways, bogs, kitchens, and living areas require focused diversifications that address mobility, sensory, and ergonomic challenges. Incorporating durable, low-maintenance materials and good applied sciences enhances day-to-day usability and emergency readiness. Adherence to building codes and skilled assessments ensures legally compliant, tailor-made options that improve long-term property worth and cut back healthcare costs.
Practical Next Steps to Facilitate Aging in Place
Start with an intensive in-home assessment by a licensed aging-in-place specialist or occupational therapist to identify customized modification wants. Prioritize high-impact adjustments that scale back fall risk and enhance accessibility, such as installing seize bars, widening doorways, and enhancing lighting. Explore local and federal funding choices, together with grants or reformas Residenciais tax incentives, to offset prices. Develop a phased renovation plan that balances budget constraints with quick safety requirements. Engage licensed contractors acquainted with accessibility standards to ensure quality workmanship. Finally, incorporate good residence options steadily, guaranteeing residents become snug with new technologies whereas maintaining management and independence.